📌 Factuality and Hallucinations in Google’s AI-Driven Search
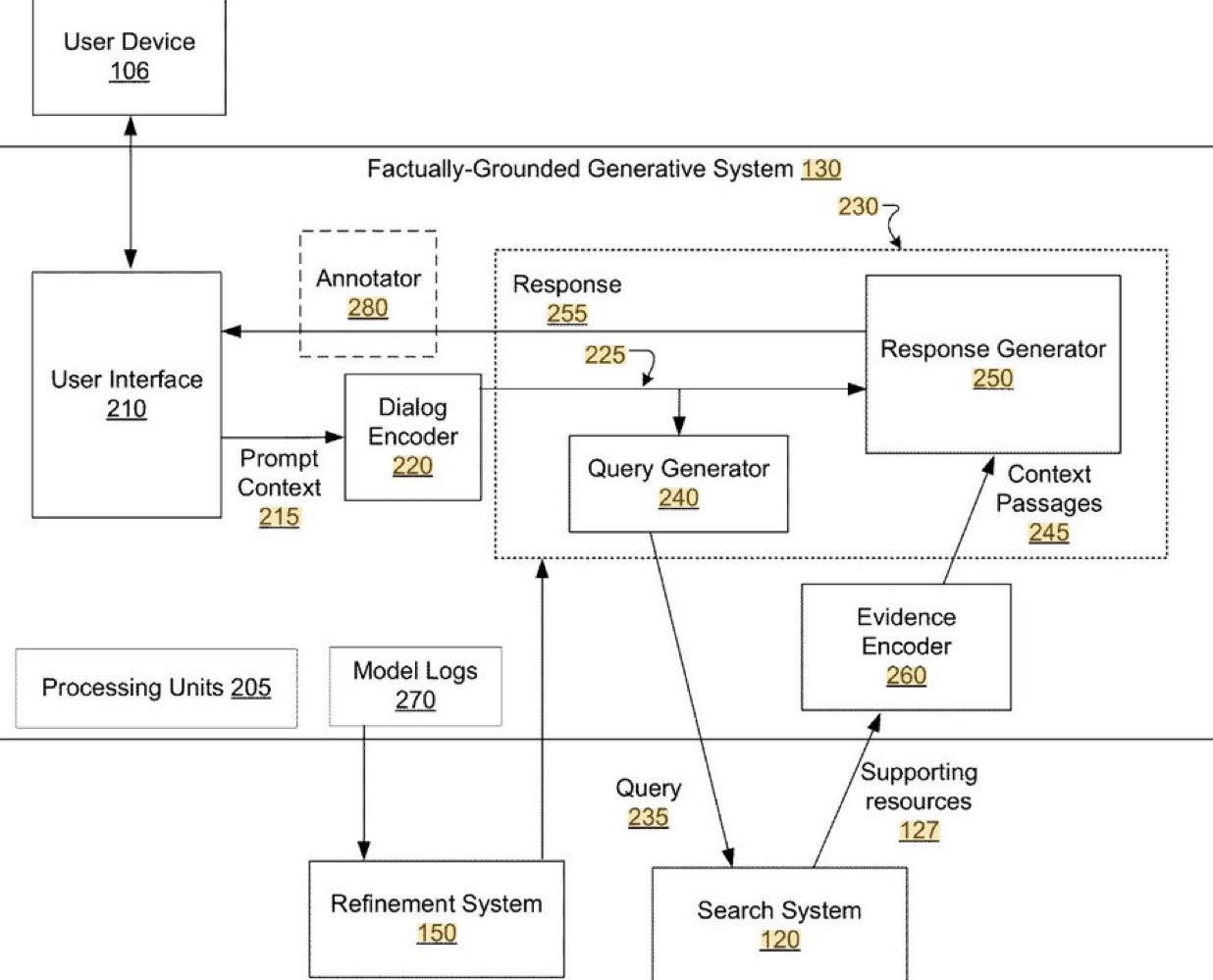
Google refers to factually incorrect generated content as a hallucination. To reduce these hallucinations while preserving creative flexibility, Google’s systems use a multi-step process:
- 🔹 A large language model (LLM) takes the conversation context (prompt) as input
- 🔹 It identifies search queries based on that context
- 🔹 Retrieves search results in real time
- 🔹 Feeds both the conversation context and the retrieved results back into the model
Through fine-tuning, the model learns when to use search results and which ones to prioritize—reducing hallucinations and increasing response accuracy.
In simpler terms, Google’s implementation is designed to prevent LLMs from stating “facts” that are unsupported by evidence. This includes mechanisms for proper attribution and citation.
🧠 This challenge isn’t new. When Google first introduced Featured Snippets nearly 7 years ago, factuality was a core concern. It’s the same with Search Generative Experience (SGE).
⚠️ The issue: Google’s AI Mode can introduce significant factuality risks.
✅ The solution: Double down on accuracy and consensus.
From a content creation and SEO standpoint:
- Factuality depends on sentential semantics, which are computationally expensive.
- Therefore, high-PageRank sources and those with brand-driven search demand gain priority.
- Smaller but uniquely valuable sites may still find traction—especially in niche conversations on new AI-driven SERP surfaces.
Also worth noting: Google’s patents are increasingly using the term “conversation” rather than “query” — a subtle but telling shift in how search is evolving.
Want to future-proof your content?
- ✅ Focus on semantic precision
- ✅ Ensure your claims are evidence-supported
- ✅ Structure information for retrievability & attribution
