Semantic Search Patterns
🧠 You can't build a semantic content network without understanding the semantic search patterns of your target users.
🔍 There are patterns in how users search for information.
🔗 And there are relations in the words they use to search for that information.
✨ Based on the predicates (verbs) used in the queries, the themes will be different.
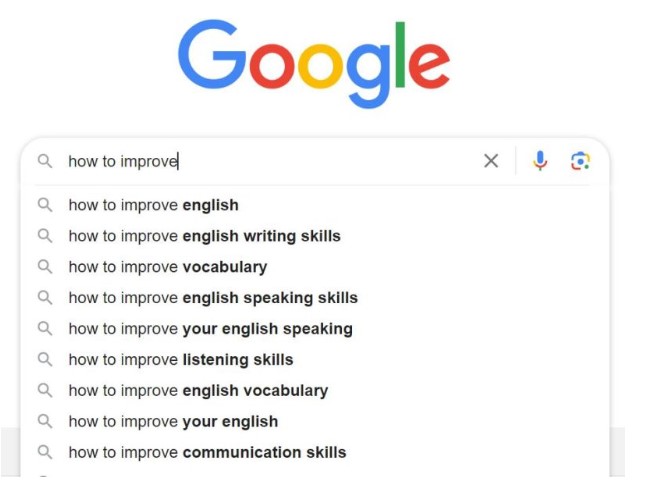
📌 Example Query:
"How to improve X"
The nouns replacing "X" should have a thematic similarity due to the predicate "improve."
🟢 Google auto-completes the following nouns for "X":
- 🌴 English
- 🌴 English Writing Skills
- 🌴 Vocabulary
- 🌴 Listening Skills
- 🌴 Communication Skills
📌 Any change in the predicate will result in a change to the overall theme.
🔄 Google auto-complete would also vary based on different predicates.
❓ But why are predicates so important?
A semantic search engine organizes its index and processes queries based on the EAV (Entity, Attribute, Value) database structure.
📚 This EAV model relies on predicates to distinguish contexts and subtopics.
That’s why understanding the verbs in a query is so crucial.
🧩 These verbs help build a semantic content network by signaling the thematic words.
☕ Take the example of the noun "coffee":
When paired with different verbs (predicates), the thematic direction changes:
✅ "Brewing coffee" signals:
- 🔸 Grinder
- 🔸 Filter
- 🔸 Kettle
- 🔸 Beans
- 🔸 Barista
✅ "Growing coffee" signals:
- 🔸 Plantation
- 🔸 Farmer
- 🔸 Harvest
- 🔸 Beans
- 🔸 Soil
🔍 All such thematic words appear based on the verb affecting the noun (in this case, "coffee").
🧠 Why this matters:
Understanding search patterns helps you plan your semantic content network more effectively.
It lets you factor in user behavior and intent, giving your content a strategic SEO edge.
